The design of a mixer settler plays a crucial role in determining its efficiency and effectiveness in separating different components during liquid-liquid extraction processes. Several design factors influence these aspects:
Phase Contacting Mechanism:Mixer settlers are designed to facilitate intimate contact between two immiscible liquid phases (such as aqueous and organic phases). The efficiency of phase contacting is influenced by the design of the mixing and settling zones within the unit.
Efficient mixing ensures thorough dispersion of the phases, maximizing the surface area for mass transfer and enhancing the contact between the components to be separated.
Mixing Intensity and Time:The design determines the intensity and duration of mixing provided to the phases. Proper mixing intensity promotes rapid and uniform distribution of components between the phases.
Optimal mixing time allows sufficient interaction between the phases for mass transfer to occur effectively, ensuring that the desired components are adequately transferred from one phase to another.
Settling Zone Design:After mixing, the settling zone allows the phases to separate based on their density differences. The design of the settler zone affects the settling efficiency and the clarity of the separated phases.
Effective settling zones have sufficient residence time and space for phase separation, minimizing carryover of one phase into another and improving overall separation efficiency.
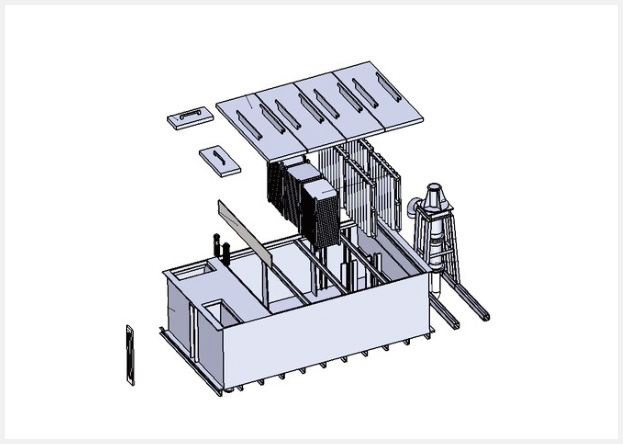
Internal Configuration and Flow Dynamics:The internal configuration, including the shape, size, and arrangement of internal components (such as baffles or plates), influences flow dynamics within the mixer settler.
Properly designed internal components help in controlling flow patterns, avoiding short-circuiting of phases, and maximizing residence time, which are critical for efficient separation.
Scale and Capacity:The size and capacity of the mixer settler unit impact its throughput and operational efficiency. Larger units can handle higher volumes of liquid and may have multiple stages or compartments to enhance separation efficiency.
Scaling considerations ensure that the design parameters (such as mixing intensity, settling time, and phase distribution) are maintained across different sizes to achieve consistent performance.
Material Selection and Construction:The choice of materials for construction must consider compatibility with the process fluids, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Proper material selection ensures durability and reliability of the mixer settler over its operational life.
Control and Automation:Advanced designs may incorporate control systems or automation to monitor and optimize process parameters such as flow rates, temperature, and phase ratios. Automated systems can adjust operational settings in real-time to maximize efficiency and maintain separation performance.
The design of a mixer settler directly impacts its efficiency and effectiveness in separating different components by optimizing phase contact, mixing intensity, settling characteristics, internal flow dynamics, and overall operational parameters. A well-designed mixer settler enhances mass transfer rates, minimizes losses, improves product purity, and ensures reliable performance in liquid-liquid extraction processes across various industries.